Search Results
Showing Results for Advanced Parkinson’s disease
Dr Bedia Samanci is a 2025 touchNEUROLOGY Future Leader, and is already making a significant impact in the field of clinical neurology. In this Q&A we discuss advanced neuroimaging, biomarker discovery and the integration of machine learning into neurological diagnostics. Areas that promise to shape the future of patient care.
Prof. Joaquim Ferreira shares insights from EAN 2025 on the future of Parkinson’s disease care. He discusses realistic timelines for DMTs, the evolving role of gene therapy for genetic subgroups, and the potential of adaptive deep brain stimulation. Prof. Ferreira also highlights the growing importance of optimizing current treatments, interdisciplinary care, and addressing persistent challenges such as gait disturbance, dyskinesia, and cognitive decline.

At EAN 2025, Prof. K. Ray Chaudhuri shares insights into cutting-edge Parkinson's drug delivery methods, the future of biomarker-driven care, advances in managing sleep disturbances, and the vital role of lifestyle modifications in optimizing patient outcomes.

Explore ground-breaking advancements in the treatment of movement disorders in this insightful interview with Prof. K. Ray Chaudhuri, who shares his key takeaways from the 10th Congress of the European Academy of Neurology meeting in Helsinki. He discusses promising new therapies, personalized care approaches, and significant research on the staging of Parkinson's. Additionally, Prof. Chaudhuri emphasizes the importance of holistic treatment, stepped-care strategies, remote management, and the potential of wearable technology in improving patient outcomes, bringing his wealth of knowledge and insights to touchNEUROLOGY

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a complex neurodegenerative condition that predominantly affects older people, with a rising prevalence worldwide.1,2 There are many on-going challenges and unmet needs in PD: difficulties in making an accurate diagnosis (particularly in the early stages ...

Welcome to the latest edition of touchREVIEWS in Neurology. We are excited to present a collection of articles that showcase the latest advancements and diverse perspectives in neurological research and treatment. This issue features insightful reviews and editorials from esteemed ...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is characterized by prodromal and clinical stages; the clinical phase is characterized by a constellation of motor and non-motor symptoms (NMS).1 Despite the extensive discussions and publications of the clinical heterogeneity of PD,2 the precise heterogeneous ...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a chronic progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the degeneration of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons, with its incidence increasing globally.1 With disease progression, the benefit from medications shortens, and symptom control becomes strictly dependent on peripheral levodopa (...
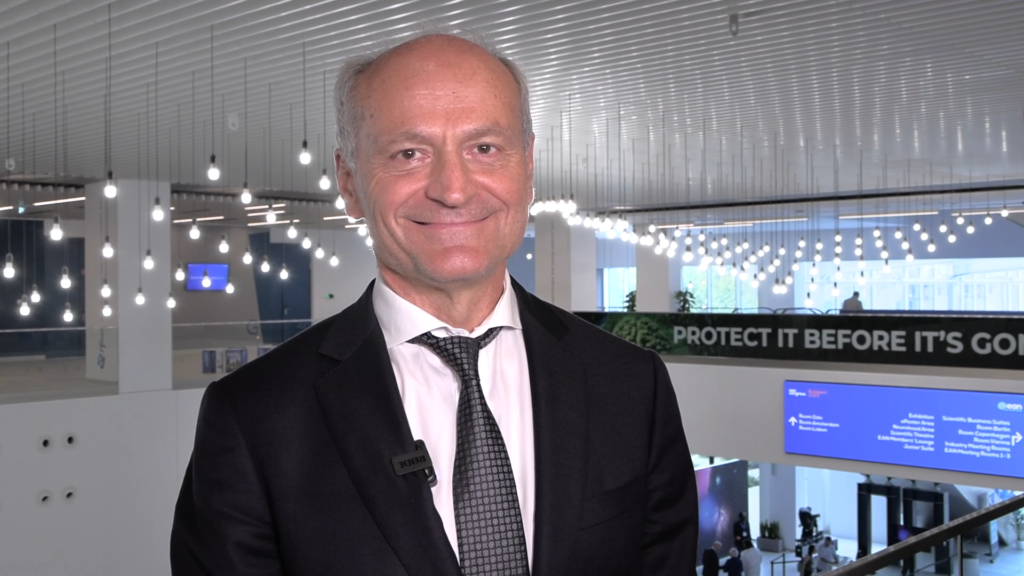

touchNEUROLOGY editorial board member Prof. Angelo Antonini (Padua University Hospital, Italy) provides an overview of his top three most important updates and hot topics from the annual European Academy of Neurology (EAN), July 1–4, 2023, in the field of Parkinson's disease. He ...

In modern medicine, the concept of wellness is accompanied by many misconceptions. Adopting wellness as a treatment approach has been well defined and implemented in cardiovascular disease, diabetes and some types of cancer management but has not yet been widely ...

Gastrointestinal dysfunctions represent one of the main non-motor symptoms in Parksinon’s disease (PD). Prof. Angelo Antonini (Professor of Neurology, University of Padua, Padua, Italy) discusses a study that investigated α-Synuclein seeding activity in stomach-duodenum biopsies of PD patients by ...

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive, neurodegenerative movement disorder and the second most common neurodegenerative disorder in the United States.1 In 2020, approximately 930,000 people in the United States aged 45 years and older developed the disease, and this number is expected ...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive, neurodegenerative disorder that causes a range of motor and non-motor symptoms. The pathological hallmark of PD is the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta of the midbrain and the ...
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive synucleinopathy that causes widespread neurodegeneration.1 It is estimated to affect approximately 6.1 million people globally and 0.7–1.0 million people in the USA.2–4 The incidence of the disease is expected to continue to increase over time, and ...
Parkinson’s disease is now considered to be a spreading disease caused by the aggregation of abnormal alpha-synuclein.1 According to Braak et al., in stage I of the disease, alpha-synuclein pathology is found in the olfactory bulb and the dorsal ...
Neuropathic pain arises from injury to or disease in the somatosensory nervous system.1 Normal sensation and pain sensation are both impaired and patients may present with peculiar painful characteristics such as allodynia and hyperalgesia.2 Central neuropathic pain includes pain from ...

We were fortunate to have the opportunity to speak with Tanya Simuni (Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, IL, USA) following her session entitled: Update on Recent Clinical Trials - Parkinson's Disease. Questions 1. Could you give us a brief ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.


