Search Results
Showing Results for Basal ganglia
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a neurodegenerative disease inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. It is caused by an expansion of cytosine, adenine, guanine (CAG) repeats within the huntingtin (HTT) gene, which is located on chromosome 4. This pathological expansion of ...
Diabetic striatopathy (DS) is a rare hyperglycaemic condition associated with one or both of the following criteria: (1) acute-onset chorea–ballism (random, flowing and nonsuppressible involuntary movements) and (2) striatal hyperdensity on computed tomography (CT) scan or T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (...
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is an effective treatment that significantly reduces disabling levodopa-induced motor complications (i.e. dyskinesia and motor fluctuations) and tremor in individuals with Parkinson’s disease (PD).1,2 During DBS, electrical stimulation is delivered through stereotactically implanted electrodes ...

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive, neurodegenerative movement disorder and the second most common neurodegenerative disorder in the United States.1 In 2020, approximately 930,000 people in the United States aged 45 years and older developed the disease, and this number is expected ...
Phenomenology and clinical significance of OFF episodes in Parkinson’s disease Werner Poewe Department of Neurology, Innsbruck Medical University, Innsbruck, Austria The emergence of OFF episodes in Parkinson's disease (PD) marks the transition from the so-called ‘honeymoon’ period of good ...
Following approval in Europe in 2015 and in the USA in 2017,1 and its subsequent introduction, safinamide has become established as an effective and well-tolerated add-on to levodopa treatment in Parkinson’s disease (PD). Despite the extensive clinical trial data and a ...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is classically defined as a movement disorder with key features including motor disturbances such as tremor, rigidity, akinesia and postural instability. Non-motor symptoms are also present, and can include disturbances in autonomic function, sleep, cognition, sensory ...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a multifaceted neurodegenerative disease that progressively affects individuals’ mobility. In addition to the cumulative motor disability, a plethora of non-motor symptoms (NMS-PD) can be encountered at different stages of the disease. Some of these NMS-PD ...

The burdens of Parkinson’s disease (PD) are undeniably serious and increasing while various unmet needs remain, especially the absence of disease-modifying therapies and the difficulty of finding new treatments that are effective in patients.1–7 Although this seems a discouraging ...
Overview of topics covered in this review Glutamate and the basal ganglia in the healthy brain Glutamate and glutamate receptors – role in motor circuitry The basal ganglia – anatomy and function The basal ganglia pathways and the role of glutamate in ...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopamine production in the substantia nigra. While oral therapies can effectively augment the dopaminergic pathway, their effect lessens as the disease progresses, and patients require multiple ...
The occurrence of mixed dementias is significantly related to the aging process.1 Their brain pathology accounts for most cases in community-dwelling older persons.2 Mixed dementias are clinically under-recognised and need neuropathological confirmation.3 The most frequent types are those composed ...

The ‘overarching theme’ of this year’s 4th Congress of the European Academy of Neurology (EAN), which was held from 16–19 June 2018 in Lisbon, Portugal, was neurogenetics, a rapidly expanding field. This theme was reflected in numerous presentations, workshops and symposia. ...
Optimising the effect of dopaminergic treatment in Parkinson’s disease Presented by: Werner Poewe Department of Neurology, Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria In considering dopaminergic treatment of Parkinson’s disease (PD), one must consider dopaminergic drug targets, effect sizes of ...

Pick complex refers to a spectrum of diseases with a variety of overlapping and pathological features. Although not ubiquitous, the presence of tau inclusions is a common feature in Pick complexes.1 The main neuropathological phenotypes comprise tau-frontotemporal lobar degeneration (tau-FTLD), ...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, with a prevalence that increases with age: 41 in 100,000 in the age group 40–49, rising to 1,903 in 100,000 in those aged over 80 years.1 PD is characterised by striatal dopamine deficiency resulting from progressive degeneration ...

Overview of Parkinson’s disease Epidemiology Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a common, chronic and progressive neurological condition. It is estimated to affect 100–180 people per 100,000 of the population and has an annual incidence of 4–20 per 100,000 people.1 The prevalence of PD ...
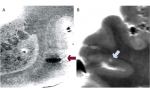
Although post-mortem neuropathological examination is increasingly performed less often in most western countries, it is still needed in patients with dementia, due to neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular changes, It is important for the family to be sure about the clinical diagnosis ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.

