Search Results
Showing Results for embolic stroke

Welcome to the latest edition of touchREVIEWS in Neurology. We are excited to present a collection of articles that showcase the latest advancements and diverse perspectives in neurological research and treatment. This issue features insightful reviews and editorials from esteemed ...
Introduction The term 'stroke' is used to describe an adverse clinical state involving interference of blood circulation to the brain due to obstruction or rupture of blood vessels.1 Stroke was previously categorized into a cardiovascular disorder until the release of ...

Ischaemic stroke may occur due to several potential mechanisms. Mechanisms are classically described as large artery atherosclerosis, small-vessel occlusion, cardioembolism, stroke of other determined aetiology (i.e. vasculitis, genetic disorder, etc.) and stroke of undetermined aetiology. Historically, the definition of ...
Healthcare workers are currently facing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and its complications, caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). Patients usually suffer from respiratory problems and non-specific neurological symptoms, such as headache, dizziness and ataxia, as well as ...
Globally, a high proportion (around 25%) of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) and ischemic strokes are cryptogenic.1,2 The Trial of ORG 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) classification defines a cryptogenic stroke as a brain infarction that is not caused by definite cardioembolism, ...
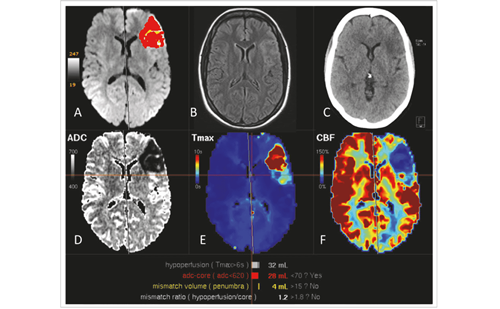
In 2018, two randomised controlled trials, DAWN (the Clinical Mismatch in the Triage of Wake up and Late Presenting Strokes Undergoing Neurointervention with Trevo Thrombectomy Procedure) and DEFUSE 3 (Endovascular Therapy Following Imaging Evaluation for Ischaemic Stroke 3), implemented computed tomography (CT) and ...

According to the World Health Organization and other leading stroke experts, stroke claims 6.2 million lives each year, and its incidence is growing.1 Although more common in the elderly, stroke also affects young adults (less than 45 years of age) and the ...

Neuroprotective Strategies in Traumatic Brain Injury Peter JD Andrews Western General Hospital NHS Trust and University of Edinburgh, UK Any severe trauma to the brain results in the activation of a cascade of biochemical pathways and release of chemical mediators. ...

Currently there is a tremendous amount of research interest in acute reperfusion therapy for patients suffering from acute ischemic stroke. However, other aspects of patient care in acute and subacute stroke are typically considered routine and thus have received less ...
About 20% of all brain infarcts are caused by atherothrombotic macroangiopathy.1,2 The prevalence of atherosclerotic carotid disease increases with age. Epidemiological data show a prevalence of 3.1% for men and 0.9% for women in individuals with ≥70% North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) ...
In atrial fibrillation (AF), considerable harm can result from the lack of appropriate preventive therapy, and optimal prevention is critical, especially in vulnerable elderly or frail patients. AF markedly increases the risk of stroke and this condition must be monitored ...
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is an opening or flap in the atrial septum that exists as a normal and vital component of intrauterine life. PFO allows for the transportation of rich oxygenated blood to bypass the lungs and flow from ...
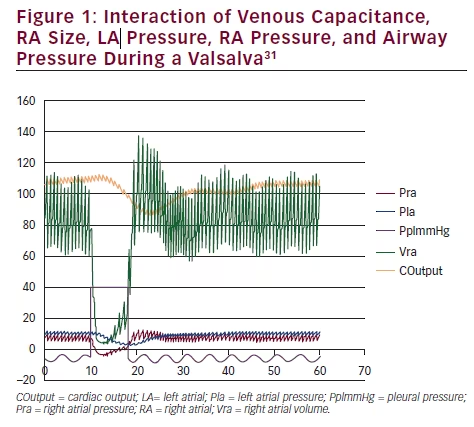
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is an opening or flap in the atrial septum that exists as a normal and vital component of intrauterine life. PFO allows for the transportation of rich oxygenated blood to bypass the lungs and flow from ...

Atrial fibrillation (AF), the most common type of cardiac arrhythmia, substantially increases the risk and severity of stroke and has a highly negative effect on patient outcomes. AF is associated with a pro-thrombotic state and studies have shown it increases ...
Cortical superficial siderosis (cSS) of the central nervous system is considered a rare condition, observed on gradient echo T2*- weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as a typical signal hypointensity outlining the brain surface. It is detected as a characteristic ...
Surgery for Occlusive Atherosclerotic DiseaseExtracranial-intracranial (EC-IC) bypass for revascularisation in the setting of atherosclerotic occlusive disease has remained a topic of intense interest and scrutiny over the last four decades. The underlying premise of EC-IC bypass in this setting is ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.