Search Results
Showing Results for intracranial aneurysm
The prevalence of unruptured intracranial aneurysms (IAs) is approximately 3% of the population, with incidence on the rise due to the increased utilization of neuro-imaging for diverse objectives.1,2 The average risk of rupture for unruptured IA is estimated to vary from 0.3% ...

Ischaemic stroke may occur due to several potential mechanisms. Mechanisms are classically described as large artery atherosclerosis, small-vessel occlusion, cardioembolism, stroke of other determined aetiology (i.e. vasculitis, genetic disorder, etc.) and stroke of undetermined aetiology. Historically, the definition of ...
Globally, a high proportion (around 25%) of transient ischemic attacks (TIAs) and ischemic strokes are cryptogenic.1,2 The Trial of ORG 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST) classification defines a cryptogenic stroke as a brain infarction that is not caused by definite cardioembolism, ...
In March 2017, a mini-symposium at the 11th Congress of Controversies in Neurology (CONy), Athens, Greece, was dedicated to neuro-Behçet’s disease (NBD). An introduction into the key clinical features of Behçet’s disease (BD) was followed by a ...

Neuroprotective Strategies in Traumatic Brain Injury Peter JD Andrews Western General Hospital NHS Trust and University of Edinburgh, UK Any severe trauma to the brain results in the activation of a cascade of biochemical pathways and release of chemical mediators. ...
Targeted Temperature Management as the Standard of Care – Aligning Practice, Evidence and Guidelines
Scope of the fever problem in the neurological intensive care unitPresented by Stephan A MayerNeurocritical Care, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York City, New York, US Fever-related brain injury in the neurological intensive care unit (NICU) has ...
Identifying secondary headaches in the emergency room In 2008 alone (according to most recent data), there were over 3 million visits to the emergency room (ER) where headache was the primary complaint, in the US.1 Headache comprised a little over 2% of all ...
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is an opening or flap in the atrial septum that exists as a normal and vital component of intrauterine life. PFO allows for the transportation of rich oxygenated blood to bypass the lungs and flow from ...
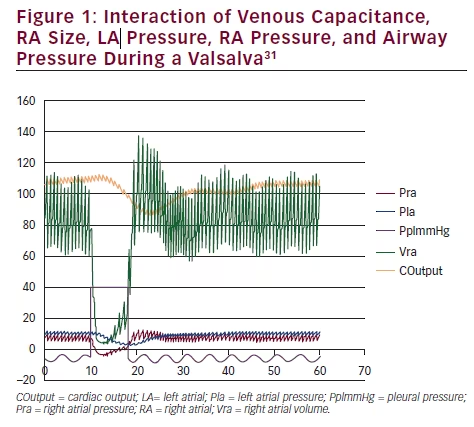
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is an opening or flap in the atrial septum that exists as a normal and vital component of intrauterine life. PFO allows for the transportation of rich oxygenated blood to bypass the lungs and flow from ...

Spontaneous intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) is defined as a focal collection of blood within the brain parenchyma or ventricular system that is not caused by trauma.1 It is a heterogeneous condition resulting from several distinct underlying vasculopathies. Several interacting and overlapping ...
Headache is the most common somatic complaint seen in the emergency department, accounting for 1 % to 3 % of all emergency department visits.1 Given the range of headache-related disorders, a systematic approach to headache classification and diagnosis is essential for best clinical management.2 ...

Stroke is the second most common cause of death and a major cause of disability worldwide. Because of the ageing population, the burden of stroke is likely to increase during the next 20 years, especially in developing countries.1 The majority (85 %) of ...

A tremendous amount of research effort has been put into the understanding and treatment of delayed cerebral vasospasm and its sequelae, namely the development of delayed ischaemic neurological deficits (DIND), since it contributes significantly to overall morbidity and mortality after ...

The treatment of intracranial aneurysms, both ruptured and unruptured, has witnessed a dramatic improvement in outcomes made possible by continuous refinement in microsurgical technique alongside major technological developments and a growing understanding of the physiology of the brain under normal ...

Surgery for Traumatic Brain Injury Surgery for Traumatic Brain Injury The surgical treatment of traumatic lesions in head injury can be challenging and complex, both in terms of indication and technique. Most procedures in neurotrauma are, however, performed by young ...

The vertebral artery (VA) is a branch of the subclavian artery, which runs along the cervical spine and ends intradurally at the junction with the basilar trunk. It is subdivided into four segments: V1 segment (ostial segment) from origin to ...

What Is Constructive Interference in Steady State Imaging? What Is Constructive Interference in Steady State Imaging? Constructive interference in steady state (CISS) imaging is a member of the family of fast gradient echo (GRE) sequences. The CISS sequence is particularly ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.


