Search Results
Showing Results for neural stem cells
Affecting over 70 million patients worldwide, epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by intermittent bursts of hyper-synchronous neuronal discharges.1 The manifestations are variable but reflective of the unique milieu and biology of epileptogenic foci.2 Pharmacological treatment with antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) ...
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is a rare inflammatory autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS) with a worldwide distribution.1 The first clinical description of NMOSD was made a century ago by Devic and Gault, who documented patients with ...
Introduction The term 'stroke' is used to describe an adverse clinical state involving interference of blood circulation to the brain due to obstruction or rupture of blood vessels.1 Stroke was previously categorized into a cardiovascular disorder until the release of ...
It cannot be seen, cannot be felt, cannot be heard, cannot be smelt. It lies behind stars and under hills, and empty holes it fills. It comes first and follows after, ends life, kills laughter. The Hobbit. JRR Tolkien ‘Darkness’ ...
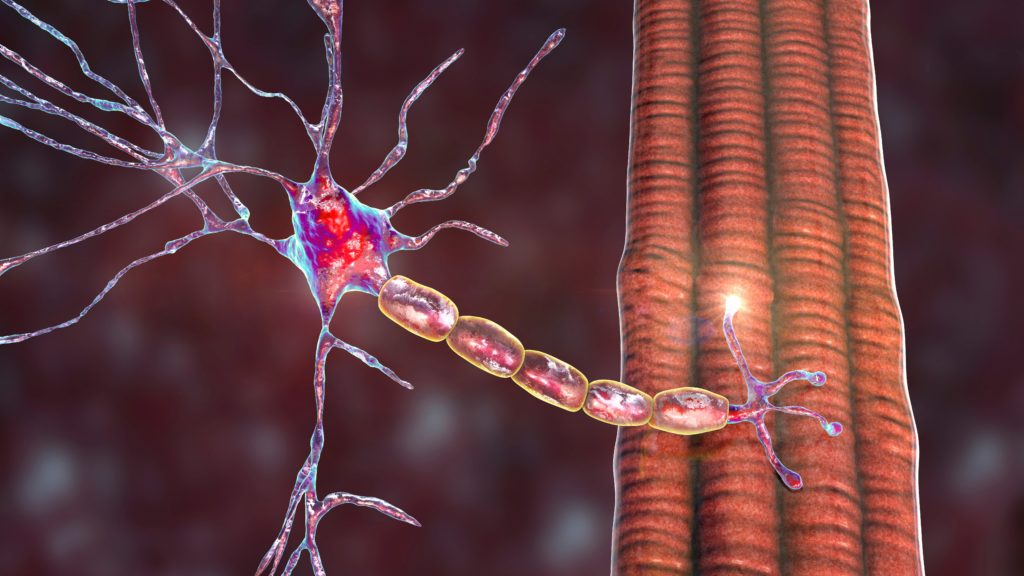
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disorder caused by autoantibodies against the myoneural junction, which lead to impaired neuromuscular transmission. These antibodies act at the post-synaptic membrane, commonly against the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) but in some cases, antibodies to ...
In the past 4 months, a novel coronavirus originating in Wuhan, China, SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2), has affected more than 200 countries. As of mid-June 2020, there are over 7 million confirmed cases and more than 425,888 deaths worldwide caused by the novel ...
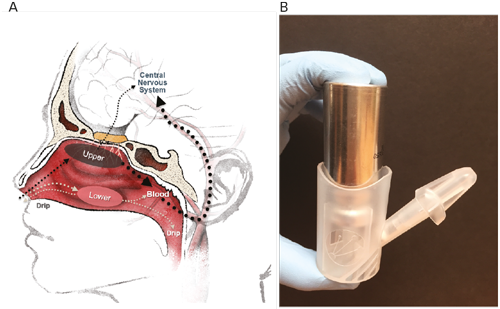
Treatment of acute central nervous system (CNS) conditions requires effective drugs that can provide rapid onset of effect, consistent blood levels, ease-of-use for patient or caregiver, and acceptable tolerability. Solid oral dosage forms account for up to 75% of prescriptions from ...
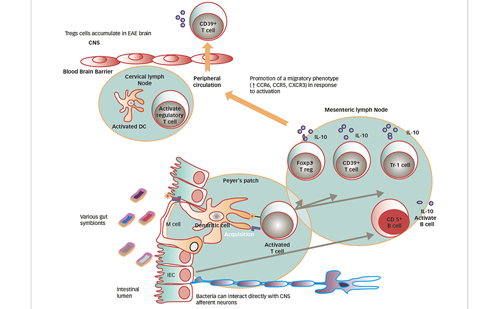
Multiple sclerosis (MS) involves inflammation, demyelination and neurodegeneration of the central nervous system (CNS) and is characterized by variable degrees of axonal loss and gliosis.1 Lesions occur in both the white and grey matter. Generally, the overall incidence of MS ...

A growing body of evidence has highlighted the role of neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of many neurological diseases. While neuroinflammation has been well characterised in some conditions, notably multiple sclerosis, it is now known to play a role in diseases ...
Overview of topics covered in this review Glutamate and the basal ganglia in the healthy brain Glutamate and glutamate receptors – role in motor circuitry The basal ganglia – anatomy and function The basal ganglia pathways and the role of glutamate in ...
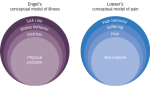
Chronic pain is a widespread, debilitating condition shared by millions worldwide. In 2015, more than 25 million Americans reported suffering from consistent daily pain.1 The Center for Disease Control (CDC) reported 15.6% of American adults experience consistent headaches or migraines, 29% have consistent low ...
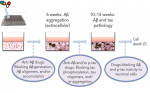
Recapitulating Amyloid β and Tau Pathology in Human Neural Cell Culture Models—Clinical Implications
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease, clinically characterized by progressive memory loss. To date, an estimated 5.2 million people have the disease in the US, and the total number of people with AD-related dementia is projected to ...

Vitamin D is an essential nutrient for bone homeostasis that has also been implicated in numerous other disorders, such as cardiovascular disease (CVD) and autoimmune diseases. Originally vitamin D deficiency was associated only with rickets and it was considered that ...
Understanding MS Better in 2014Contribution of Epidemiological factorsMultiple sclerosis (MS) is considered to be an immune-mediated neuro-inflammatory and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system (CNS) with heterogeneous clinical presentation and course, neuroimaging and pathological findings. Several genetic and environmental ...
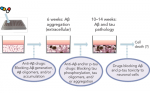
Recapitulating Amyloid β and Tau Pathology in Human Neural Cell Culture Models—Clinical Implications
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease, clinically characterized by progressive memory loss. To date, an estimated 5.2 million people have the disease in the US, and the total number of people with AD-related dementia is projected to ...
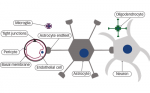
Cognitive impairment (CI) is frequently associated with critical illness and can be defined as the loss or decline of higher mental functions (memory, attention, calculation, language, orientation and speed of information processing) that modify a person’s activity and social ...

Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a condition with many unmet needs in medicine and public health.1,2 It is a major cause of death and disability and also leads to extremely high direct and indirect costs to society.3–5 Currently the incidence ...

First described by Willis in 1672 and described in more detail by Ekbom in 1945, restless legs syndrome (RLS) or Willis–Ekbom disease (WED) is defined as a sensorimotor disorder in which the initial sensory symptom consists of an irresistible urge to ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.

