Search Results
Showing Results for phenobarbital

Seizures are one of the most frequent neurological disorders in neonates − the incidence of seizures in infants born at term is 1–3 per 1,000 live births, and is even higher in both preterm and very-low-birth-weight infants at 1–13 per 1,000 live births.1 Seizures may ...
A new guideline has been issued to assist neurologists and clinicians in selecting the best anti-seizure medications for people with epilepsy who may become pregnant. Published in Neurology, the guideline is a collaboration between the American Academy of Neurology (AAN), the American Epilepsy Society (AES) and the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine (SMFM), with endorsement from the Child Neurology Society. It updates parts of the 2009 AAN and AES guidelines regarding birth malformations and child development in children born to people with epilepsy.
Epilepsy is a very common neurological disease, affecting more than 50 million people worldwide and 3.4 million people in the USA.1–3 Focal seizures, formerly partial-onset seizures, are the most common type, making up ≥60% of cases.4–6 Patients with epilepsy have an increased risk ...

Epilepsy is one of the most common neurological disorders, affecting around 70 million people worldwide.1,2 Its management is mainly symptomatic, and long-term seizure remission is achieved in most cases.3,4 One-third of patients, however, continue to experience seizures despite adequate treatment.5 Remarkably, ...

Neuroprotective Strategies in Traumatic Brain Injury Peter JD Andrews Western General Hospital NHS Trust and University of Edinburgh, UK Any severe trauma to the brain results in the activation of a cascade of biochemical pathways and release of chemical mediators. ...
As the armamentarium of anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) continues to expand, epilepsy management is becoming increasingly complex. This necessitates multiple considerations for the choice of the most appropriate AED that can broadly be organised into five categories: (i) rational treatment selection (...
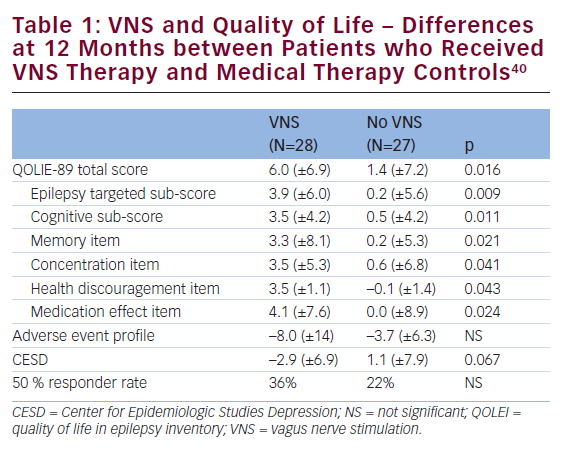
Epilepsy is one of the most common serious neurological conditions, has no geographic, social or racial boundaries and can affect people of all ages.1 It is frequently associated with co-morbidities, not just seizures, and is a condition that is linked ...
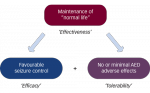
Epilepsy is one of the most common serious neurological disorders and has far-reaching consequences, not only for patients living with the condition, but also for their families and society as a whole.1 It is useful therefore to evaluate whether the ...

Epilepsy is a general term used to describe a collection of common, chronic conditions of recurrent and unpredictable seizures. While seizures in newly diagnosed patients are often controlled with a single antiepileptic drug (AED),1 the estimated 30–40 % of patients who are ...

Homocysteine – A Marker for Vitamin Deficiency and a Risk Factor for Neurological Diseases Homocysteine – A Marker for Vitamin Deficiency and a Risk Factor for Neurological Diseases Homocysteine (Hcy) is the demethylated product of methionine. This toxic amino acid can be ...

Epilepsy is a common, complex, and chronic neurologic disorder affecting an estimated 0.5–1% of the global population or approximately 50 million people worldwide,1,2 1.1–2.3 million of whom reside in the US.3 The ultimate goal of the treatment of epilepsy is to eliminate seizures ...

For the past 30 years, a dogma of epilepsy treatment has been to start with monotherapy.1 This still makes sense for several reasons: cost, lower risk of side effects, better compliance, and avoidance of pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) drug interactions.2 ...

Homocysteine – A Marker for Vitamin Deficiency and a Risk Factor for Neurological Diseases Homocysteine – A Marker for Vitamin Deficiency and a Risk Factor for Neurological Diseases Homocysteine (Hcy) is the demethylated product of methionine. This toxic amino acid can be ...

Adequate control of partial-onset epilepsy often requires polypharmacy, either due the to less than ideal efficacy of one antiepileptic drug (AED) (see Table 1) or due to side effects caused by the initial AED (see Table 2). Up to one-third of patients ...

Several new AEDs—felbamate, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam (LEV), oxcarbazepine, tiagabine, topiramate, vigabatrin, zonisamide, and gabitril are currently available by prescription in the US. Over the past decade alone, 10 new AEDs have been introduced; the efficacy of the newer agents ...
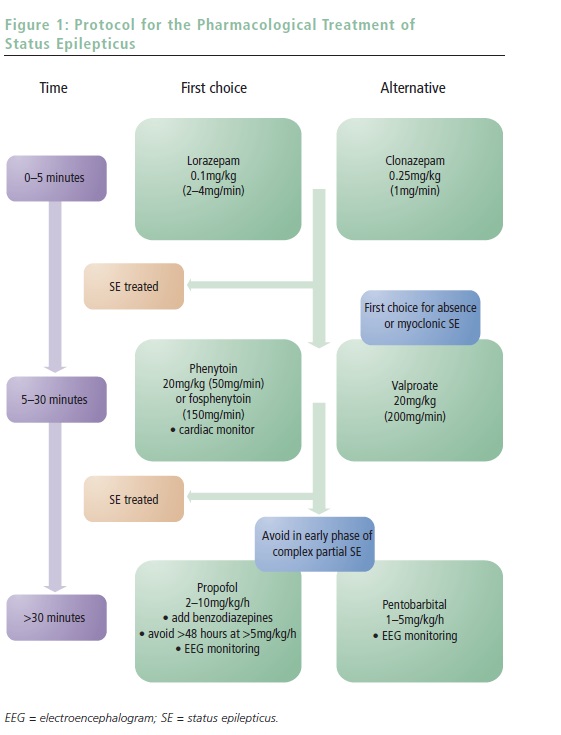
Definitions and Epidemiology An accurate diagnosis is necessary before appropriate treatment can be initiated. In contrast to most neurological entities, there is no universally accepted definition of status epilepticus (SE). Broadly speaking, SE is the occurrence of continuous seizures or ...

Although every seizure type can theoretically persist and evolve into SE, a simple 2D SE classification system can be constructed, either generalized or focal to be combined with convulsive or non-convulsive.7 While generalized convulsive SE appears straightforward, generalized non-convulsive SE ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.

