Search Results
Showing Results for rituximab

Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disorder where antibodies disrupt the neuromuscular junction, causing muscle weakness that worsens with activity. MG subgroups are based on muscle weakness location, age, antibody type, and thymus pathology, with some patients experiencing severe, treatment-resistant symptoms. Biomarkers can indicate prognosis. First-line treatments include pyridostigmine for symptomatic relief and immunosuppressants like prednisolone and azathioprine. Thymectomy is recommended for certain patients. Second-line treatments include mycophenolate, rituximab, and others, with new therapies like complement and FcRn inhibitors showing promise. Intravenous immunoglobulin and plasma exchange are used for acute exacerbations. Supportive therapy, including adapted exercise, is crucial. In refractory cases, comorbidities and diagnosis accuracy should be reconsidered.
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD) are a group of relapsing autoimmune diseases of the central nervous system. The clinical hallmarks of NMOSD are myelitis and optic neuritis; however, a wider clinical spectrum has been recognized.1 The majority of patients with ...
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is a rare inflammatory autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS) with a worldwide distribution.1 The first clinical description of NMOSD was made a century ago by Devic and Gault, who documented patients with ...
Case study Patient information A 42-year-old woman presented in the emergency department with acute onset whole-body myoclonic jerks for 1 day. On enquiry, the patient’s parents advised that she had a history of depression over the past 15 years. Intermittently, family ...
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis (ADEM), first characterized in 1931,1 is a non-specific clinical syndrome of polyfocal central nervous system (CNS) inflammatory demyelination; it is characterized by encephalopathy and large, poorly demarcated cerebral white matter lesions.2,3 Myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG) antibody-associated disease (MOGAD), ...

Over the past two decades, monoclonal antibodies targeting the surface antigen CD20 have emerged as highly effective disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) for multiple sclerosis (MS).1 The major mechanism of action of these therapies is via B-cell depletion, as CD20 is expressed ...
Paediatric-onset multiple sclerosis (POMS) is the symptom onset and diagnosis of multiple sclerosis (MS) before the age of 18.1 Diagnostic criteria were revised by the International Pediatric MS Study Group in 2013. Compared to patients with adult-onset MS (AOMS), young patients are ...
The clinical use of cancer immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) has transformed cancer management and added another effective treatment option for different types of malignancies.1–3 In 2018, the Nobel Prize for medicine and physiology was awarded for the discovery of ...
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disorder caused by autoantibodies against the myoneural junction, which lead to impaired neuromuscular transmission. These antibodies act at the post-synaptic membrane, commonly against the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) but in some cases, antibodies to ...
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) is an inflammatory disease of the central nervous system (CNS) and is known to cause recurrent episodes of optic neuritis and transverse myelitis. Myelitis is radiologically referred to as longitudinal extensive transverse myelitis on spinal ...
In the past 4 months, a novel coronavirus originating in Wuhan, China, SARS-CoV-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2), has affected more than 200 countries. As of mid-June 2020, there are over 7 million confirmed cases and more than 425,888 deaths worldwide caused by the novel ...
Neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD) refers to a family of inflammatory central nervous system (CNS) diseases in which patients accrue disability through severe episodes of demyelination with typical manifestations including involvement of visual pathways (e.g., optic neuritis) and spinal ...
Multiple sclerosis (MS) has traditionally been considered a primarily T-cell-mediated autoimmune disease of the central nervous system (CNS); this is based on data from animal models,1 the presence of activated T lymphocytes in MS plaques that outnumber B cells and ...
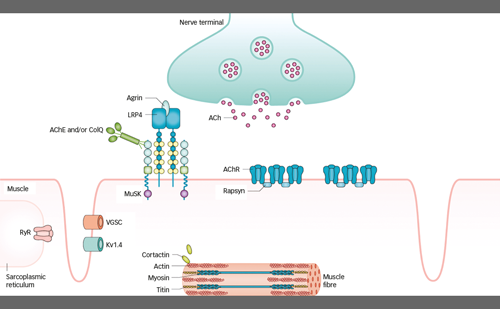
Myasthenia gravis (MG) leads to muscle weakness, which increases with repetitive use of muscles; in the morning, many patients are symptom-free.1,2 Diplopia, ptosis and weakness in other muscles innervated by cranial nerves, are typical. The muscle weakness is, in most ...

Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is a rare but challenging neuroimmunologic peripheral nerve disease with a chronic progressive or relapsing-remitting course.1,2 Effective maintenance therapies are critical for managing the condition, maintaining a response, and preventing relapse.3 In CIDP, symptoms result ...
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is an immune-mediated disorder of the peripheral nervous system, of unknown etiology.1 The condition usually presents as weakness in the arms and legs, balance/gait impairment, tingling, numbness, and loss of tendon reflexes.2–4 It can ...
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a relatively rare autoimmune disease, caused by an antibody-mediated blockade of neuromuscular transmission and resulting in skeletal muscle weakness. MG is characterised by fluctuating muscle weakness that worsens with activity and improves on resting. Over half ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.


