Search Results
Showing Results for subtype-driven care

Welcome to the latest edition of touchREVIEWS in Neurology. We are excited to present a collection of articles that showcase the latest advancements and diverse perspectives in neurological research and treatment. This issue features insightful reviews and editorials from esteemed ...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is characterized by prodromal and clinical stages; the clinical phase is characterized by a constellation of motor and non-motor symptoms (NMS).1 Despite the extensive discussions and publications of the clinical heterogeneity of PD,2 the precise heterogeneous ...

In modern medicine, the concept of wellness is accompanied by many misconceptions. Adopting wellness as a treatment approach has been well defined and implemented in cardiovascular disease, diabetes and some types of cancer management but has not yet been widely ...
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disorder caused by autoantibodies against the myoneural junction, which lead to impaired neuromuscular transmission. These antibodies act at the post-synaptic membrane, commonly against the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR) but in some cases, antibodies to ...
Siponimod—A Selective Sphingosine-1-phosphate Modulator for Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic neuro-inflammatory condition estimated to affect over two million people worldwide. Several subtypes of MS have been described, and they are defined by their clinical phenotypes.1 The majority of patients initially exhibit relapsing remitting MS (...

The medical group visit model is an innovative mode of care delivery that has gained popularity with clinicians, as it offers more options for chronic care management, with the added possibility of improving financial productivity. Group medical visits were initially ...
Introduction Presented by: Richard B Lipton Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, US Current guidelines recommend preventive treatments for people who experience frequent and disabling migraine headaches, specifically those suffering headaches on 4 or more days/month.1 However, only one-third ...
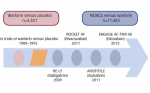
In atrial fibrillation (AF), considerable harm can result from the lack of appropriate preventive therapy, and optimal prevention is critical, especially in vulnerable elderly or frail patients. AF markedly increases the risk of stroke and this condition must be monitored ...
Understanding MS Better in 2014Contribution of Epidemiological factorsMultiple sclerosis (MS) is considered to be an immune-mediated neuro-inflammatory and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system (CNS) with heterogeneous clinical presentation and course, neuroimaging and pathological findings. Several genetic and environmental ...
Highlights of a Satellite Symposium Held at the XX World Congress on Parkinson’s Disease and Related Disorders, Geneva, Switzerland, 8–11 December 2013 Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder, characterised by motor features but is also associated with a ...

The degeneration of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal system and parkinsonism (rest tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia and postural instability/gait disorder) represent only one aspect of Parkinson’s disease (PD), a multifaceted and complex disorder.1 In addition to this typical motor dysfunction, non-motor ...

The degeneration of the dopaminergic nigrostriatal system and parkinsonism (rest tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability/gait disorder) represent only one aspect of Parkinson’s disease (PD), a multifaceted and complex disorder.1 In addition to this typical motor dysfunction, non-motor ...

Complex regional pain syndrome (CRPS) is a painful disorder of the extremities, characterised by sensory, autonomic, vasomotor, motor and trophic disturbances (see Figures 1 and 2). CRPS mostly occurs after a trauma, such as a fracture or an operation, but can also ...

The introduction of disease-modifying drugs (DMDs) during the 1990s made chronic therapies that inhibit the disease process in multiple sclerosis (MS) available to patients for the first time.1,2 While the currently available DMDs decrease the number of relapses, delay the ...

Myasthenia gravis (MG) is an autoimmune disease associated with circulating antibodies, either against the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (anti-AChR; ~80% of patients with generalised MG) or muscle-specific tyrosine kinase (anti-MuSK, 10% of patients),1 that induce a dysfunction of neuromuscular transmission owing to loss ...

The introduction of disease-modifying drugs (DMDs) during the 1990s made chronic therapies that inhibit the disease process in multiple sclerosis (MS) available to patients for the first time.1,2 While the currently available DMDs decrease the number of relapses, delay the ...

Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative condition1 affecting over 1 million people in Europe2 and North America.3 A systematic review of 25 incidence studies found that in eight studies, the mean age of symptom onset was 60–65 years, and >65 years in ...

Forty years ago, after a spate of pharmacological discoveries, diagnostic confidence was rising in psychiatry. Textbooks of the time indicated that the work of Pinel, Kraepelin and Bleuler had laid the foundation for imminent and encouraging progress in clarifying the ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.

