Search Results
Showing Results for temporal lobe epilepsy
Affecting over 70 million patients worldwide, epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by intermittent bursts of hyper-synchronous neuronal discharges.1 The manifestations are variable but reflective of the unique milieu and biology of epileptogenic foci.2 Pharmacological treatment with antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) ...
Olfactory loss has been extensively studied in Parkinson’s disease (PD) and is now widely acknowledged as one of the major non-motor symptoms of the disease, which precedes the occurrence of clinical motor symptoms.1,2 It is found in around 90% of ...

Welcome to the latest edition of European Neurological Review, which features a wide range of articles of interest to neurologists and other practitioners involved in the care of patients with neurological illness. As we move into a new decade, the ...
Seizure is a paroxysmal event caused by the excessive, hypersynchronous discharge of neurons in the brain, which causes alteration in neurologic function.1 Seizures can occur when there is a distortion between the normal balance of excitation and inhibition in the ...
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a multifaceted neurodegenerative disease that progressively affects individuals’ mobility. In addition to the cumulative motor disability, a plethora of non-motor symptoms (NMS-PD) can be encountered at different stages of the disease. Some of these NMS-PD ...
Proceedings of a symposium presented at the 13th European Congress of Epileptology, Vienna, 26th August 2018, sponsored by LivaNova. The management of patients with drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE) or treatment-resistant depression (TRD) remain serious challenges. Both conditions are common; epilepsy is believed ...
Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) is defined as a sudden, unexpected, witnessed or unwitnessed, non-traumatic and non-drowning death in a patient with epilepsy, with or without evidence of a seizure, excluding documented status epilepticus, in which post-mortem examination ...

Q. What was previously known about brainstem network validation in focal epilepsy and sudden unexplained death in epilepsy (SUDEP)? The first line of evidence for an involvement of the brainstem had come from those rare cases in whom SUDEP was ...
As the armamentarium of anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) continues to expand, epilepsy management is becoming increasingly complex. This necessitates multiple considerations for the choice of the most appropriate AED that can broadly be organised into five categories: (i) rational treatment selection (...

As its mission states, the American Epilepsy Society (AES) is working to eradicate epilepsy and its consequences. While this lofty goal may not yet be visible on the horizon, researchers and physicians who treat patients with epilepsy are making progress, ...
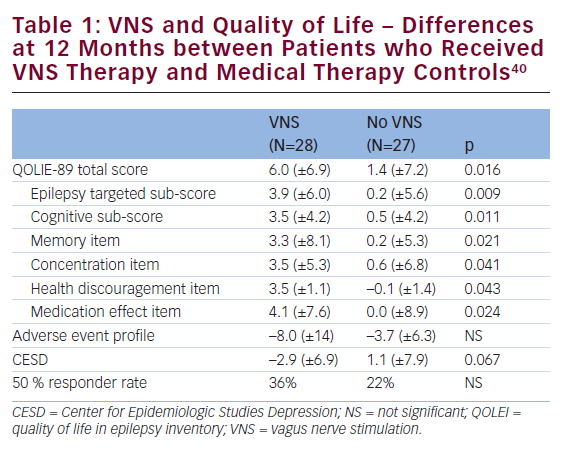
Epilepsy is one of the most common serious neurological conditions, has no geographic, social or racial boundaries and can affect people of all ages.1 It is frequently associated with co-morbidities, not just seizures, and is a condition that is linked ...

William Gower’s statement that seizures beget seizures1 is often quoted as a first recognition of seizure-dependent progressive character of epilepsies. It is worth saying that this assumption has by no means a general value as it does not apply ...

William Gower’s statement that seizures beget seizures1 is often quoted as a first recognition of seizure-dependent progressive character of epilepsies. It is worth saying that this assumption has by no means a general value as it does not apply ...

Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the most commonly used noninvasive imaging modality for epilepsy diagnosis, etiologic classification, and management. MRI is mandatory for all patients with new onset epilepsy, particularly for those who do not respond to medication. The primary ...

Epilepsy is a general term used to describe a collection of common, chronic conditions of recurrent and unpredictable seizures. While seizures in newly diagnosed patients are often controlled with a single antiepileptic drug (AED),1 the estimated 30–40 % of patients who are ...

The hippocampus plays an important role in human learning and memory and is known to be vulnerable to the effects of stress and disease.1 Within animal models of type 1 diabetes,2 significant hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia exposure has been shown to cause ...
A number of paediatric and adult neurosurgical units are investing significant resources in the development of intra-operative magnetic resonance imaging (ioMRI). In Alder Hey Hospital we have been fortunate enough to have this service available since October 2009 and so we ...
Autoantibody-mediated diseases of the central nervous system (CNS) are a rapidly expanding field within contemporary neuroimmunology. Autoimmune encephalitis (AIE) is a treatable cause of subacuteonset memory loss and confusion. In some patients, the evidence for inflammation is limited and the ...
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.

