EUROPEAN NEUROLOGICAL REVIEW – VOLUME 5 ISSUE 1 – SUMMER 2010
Foreword
We are in the midst of one of the more exciting scientific transformations of all time. The perfect storm of a digital age, non-invasive imaging, an emerging scientific culture of data sharing and an ever improving computational infrastructure has forever changed how we study the brain. Co-ordinated multisite trials where well described data are made […]
Neurodegenerative Diseases
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common cause of dementia in the elderly, with a prevalence of 5% after 65 years of age. The disease was originally described by Alois Alzheimer and Gaetano Perusini in 1906, and it is clinically characterised by progressive cognitive impairment including impaired judgement, decision-making and orientation, often accompanied, in later […]
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia and affects millions of people worldwide. The disorder is characterised by severe memory loss, with episodic memory being particularly impaired during the initial phases. Most AD cases occur sporadically, although inheritance of certain susceptibility genes enhances the risk. Familial AD represents the minority of AD […]
Oral levodopa remains the most effective symptomatic drug for Parkinson’s disease (PD); however, its long-term use is limited by the emergence of motor fluctuations and involuntary movements, particularly in young-onset patients. A growing number of preclinical and clinical studies suggest that non-physiological pulsatile stimulation of striatal dopamine (DA) receptors induced by the use of short-acting […]
There is convincing evidence from numerous studies using both psychophysical and electrophysiological approaches that olfaction is markedly reduced in Parkinson’s disease (PD). In light of the current data on smell loss in PD patients, olfactory dysfunction has to be seen as a cardinal symptom of the disease that is even more consistent than the classic […]
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is the second most common neurodegenerative disorder, affecting up to 1.5% of the American population.1 It has been estimated that up to 10% of the affected population develops the disease by 40 years of age.2 The definition of early-onset PD (EOPD) varies among studies, and usually ranges between 40 and 50 years […]
Brain Trauma
Atherosclerosis is a complex inflammatory disease process of the arterial vessels.1 Chronic and acute infections have been implicated as risk factors that increase the risk of stroke, myocardial infarction (MI) and other vascular events. However, no single pathogen is likely to be responsible for elevated vascular risk.2 More likely, the combined effect of long-term exposure […]
Post-stroke Infections – Diagnosis, Prediction, Prevention and Treatment to Improve Patient Outcomes
Up to 95% of patients have at least one relevant complication within the first three months after stroke.1 Complications impair neurological outcomes2–4 and approximately one-third of patients with ischaemic stroke die during hospitalisation due to one or more complications.5 To minimise the impact of stroke-associated adverse events, patients should be treated in specialised units where […]
Transient ischaemic attack (TIA) is common, with approximately 200,000–500,000 reported to medical attention in the US each year.1 The risk of TIA rises steeply with age, with the majority of all events occurring in people over 70 years of age.2 In contrast to major stroke, the incidence of TIA is not declining and an increase […]
High-grade glioma (HGG) is the most common type of primary brain tumour in adults and accounts for >75% of the estimated 22,070 newly diagnosed malignant primary brain tumours in the US each year.1 More than half of HGGs are glioblastoma (GBM), the most aggressive subtype. The remainder include anaplastic gliomas (AGs),1,2 such as anaplastic astrocytoma […]
Multiple Sclerosis
Patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) typically present with a clinically isolated syndrome (CIS), which eventually develops into relapsing– remitting MS (RRMS); after a varying number of years, most patients transform into secondary progressive MS (SPMS). An alternative course is primary progressive MS (PPMS), which develops more rapidly from onset and is also inevitably accompanied by […]
Overview of Disability and Walking Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis
The Extent of Cognitive Impairment in Multiple Sclerosis In his original characterisation of multiple sclerosis (MS), Jean Martin Charcot noted a loss of memory and reduced understanding,1 but this wisdom was overlooked for a century. It is only since the early 1980s that cognitive impairment in MS has begun to be scientifically investigated and understood.2
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an immune-mediated disease of the central nervous system (CNS) with inflammatory demyelinating lesions and neuronal loss that is clinically characterised by unpredictable clinical relapses, remissions and progression of disability over time.1–3 Damage occurs to the myelin sheath that surrounds and protects nerve cells; this slows down or blocks messages between the […]
Basic Concepts of Multiple Sclerosis Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a relapsing inflammatory disease of the central nervous system. It is marked pathologically by discrete areas of demyelinated brain tissue in the white matter with accompanying inflammation.1 It is now evident that axonal loss accompanies demyelination early on in the disease process.2 Cortical pathology may be […]
Niemann-Pick Disease
Niemann-Pick disease type C (NPC) is a rare and fatal neurovisceral lipid storage disorder that affects both children and adults. Whereas the disease in children is characterised by mental retardation, seizures and often rapid neurodegeneration, in adults the disease is characterised by slow cognitive decline, major neuropsychiatric illness and the development of ataxia and dystonia.1
Epilepsy
The ketogenic diet (KD) is a high-fat diet used in the management of childhood epilepsy. It was determined in the early part of last century that starvation could have a beneficial effect on seizure control.1–3 Realising that this was not practical, Wilder in 1921 suggested that designing a diet that may mimic the effects of […]
Vagus Nerve Stimulation Electrical stimulation of the 10th cranial nerve or vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) has become a valuable option in the therapeutic armamentarium of adults and children with refractory epilepsy. Since its introduction in 1989 over 50,000 patients have been treated with VNS worldwide. Efficacy, side effects and tolerability have been extensively studied. The […]
Headache
Cluster headache (CH) is, by neurological standards, a relatively common condition that affects about one in 1,000 people,1 although compared with other more common primary headaches such as migraine2 it remains rare in practice. CH has been defined in the second edition of the International Classification of Headache Disorders3 as involving recurrent attacks of severe […]
Imaging
Recent advances in functional neuroimaging techniques have revolutionised the approach to neurosurgical planning. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) techniques include blood-oxygen-level- dependent (BOLD) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) methodologies for non-invasively imaging brain activation and white matter fibres, respectively. In the last decade these techniques have evolved from purely research imaging tools used in cognitive […]
3D computed tomography angiography (3D CTA) is used to image cerebral aneurysms, steno-occlusive lesion of cerebral vessels and brain tumours. 3D CTA has become the accepted alternative to conventional intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography (IADSA) for imaging and detection of aneurysms1–5 and planning treatment. Multidetector (MD) CT allows a more precise evaluation of aneurysms with a […]
International Health
Craniopharyngiomas are epithelial tumours that arise from embryonic epithelial cells of the craniopharyngeal duct. They account for 1.2–4% of all primary intracranial neoplasms and 5–10% of intracranial tumours in children.1 Although these tumours are rarely malignant, they often grow adjacent to and distort critical neurovascular structures, particularly the visual pathways and hypothalamus, leading to significant […]
Trending Topic
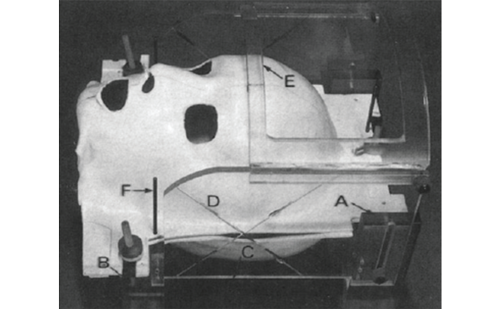
Intracranial radiosurgery, no matter the means or methods of administration, is predicated on a core set of principles, including head immobilization and precise delineation of the treatment target. For some five decades after Leksell introduced the concept of stereotactic radiosurgery in 1951,1 rigid head fixation via an invasive device was an integral component towards these ends. […]
Journal Archive
European Neurological Review is a peer-reviewed, free-to-access, bi-annual neurology journal comprising review articles, case reports, practice guides, theoretical discussions, and original research. It features balanced and comprehensive articles written by leading authorities, addressing the most important and salient developments in the field of neurology in practical terms.
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.








