EUROPEAN NEUROLOGICAL REVIEW – VOLUME 10 ISSUE 2 – WINTER 2015
Welcome to the winter edition of European Neurological Review. This edition features timely review articles and meeting reports examining a wide range of important topics. Multiple sclerosis provides a significant focus and the edition begins with two interesting reviews on vitamin D. Taylor and colleagues look at the interaction between vitamin D and interferon β-1b treatment in the BENEFIT and BEYOND studies. In the second paper, Holick and colleagues discuss the importance of screening for vitamin D deficiency and the beneficial effects of supplementation. This edition also includes articles on epilepsy, Parkinson’s disease, neuromuscular disorders and headache, all providing a worthy focus for our attention.
We hope you find this issue useful and that it provides helpful information and discussions that are relevant to your practice and interests. Please peruse and enjoy the expert content and we welcome any feedback you may have.
Welcome to the winter 2015 edition of European Neurological Review, which features a diverse range of articles covering a number of therapeutic areas. This edition begins with a series of articles and meeting reports on multiple sclerosis (MS). The articles focus on vitamin D. In the first, Taylor and colleagues look at the interaction between […]
Multiple Sclerosis
There is increasing evidence that vitamin D status is associated with both the development of multiple sclerosis (MS) and also the modulation of disease activity and possibly progression. Several publications have reported that the risk of MS is higher in patients with low vitamin D intake or serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) levels, for example due […]
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient for bone homeostasis that has also been implicated in numerous other disorders, such as cardiovascular disease (CVD) and autoimmune diseases. Originally vitamin D deficiency was associated only with rickets and it was considered that the fortification of food resolved this disorder. However, it is now realised that rickets represents […]
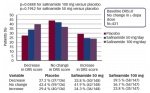
Despite the availability of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in multiple sclerosis (MS) for over 2 decades, substantial unmet treatment needs have remained. From the patient perspective, there is a need for better tolerability, quality of life (QoL) benefits and customised treatment approaches that are based on disease prognosis and individual patient needs and risk– benefit ratio. […]
Understanding MS Better in 2014Contribution of Epidemiological factorsMultiple sclerosis (MS) is considered to be an immune-mediated neuro-inflammatory and neurodegenerative disease of the central nervous system (CNS) with heterogeneous clinical presentation and course, neuroimaging and pathological findings. Several genetic and environmental factors have been shown to show some association with MS; gene–environment interactions are hypothesised to […]
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system (CNS), described by Jean Charcot in 1868. It has an estimated prevalence of 100–150/100,000 population, an annual incidence of 3.5–7/100,000 cases and typically presents at 20–40 years of age. The pathophysiology is still unclear, but immunological mechanisms seem to play an […]
Epilepsy
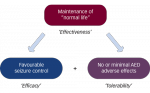
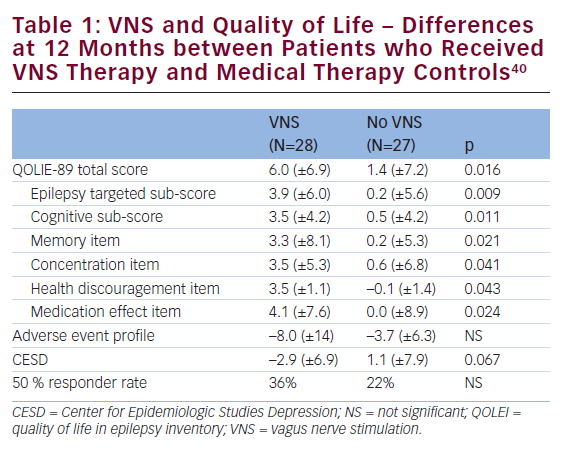
Epilepsy is one of the most common serious neurological disorders and has far-reaching consequences, not only for patients living with the condition, but also for their families and society as a whole.1 It is useful therefore to evaluate whether the advent of newer anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs) has progressed the safety and tolerability of epilepsy therapy. […]
Epilepsy is one of the most common serious neurological conditions, has no geographic, social or racial boundaries and can affect people of all ages.1 It is frequently associated with co-morbidities, not just seizures, and is a condition that is linked with a high rate of premature death compared with that in the general population.1 The […]
Parkinson’s Disease
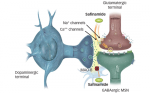
Levodopa (l-dopa) remains the most effective therapy for Parkinson’s disease (PD), but unfortunately after 3–5 years of treatment it is associated with the appearance of motor complications: motor and non-motor fluctuations (e.g. on–off phenomena, end-of-dose wearing off) and dyskinesias.1 Many non-dopaminergic transmitters, such as glutamate, have been implicated in the neural mechanisms underlying the development […]
There have been tremendous advances in understanding the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease (PD) over the past decades and the development of a range of treatments since the introduction of levodopa in the late 1960s. However, there are still significant unmet needs in the management of PD, particularly as the disease progresses, and no new classes […]
Neuromuscular Disorders
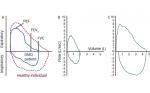
Respiratory Function Loss and Respiratory Endpoints in DMD Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most common and devastating type of muscular dystrophy. Lack of the protein dystrophin causes severe and progressive myofibre degeneration, general muscle weakness and wasting. With increasing age, DMD patients are confronted with loss of ambulation, loss of upper limb function, cardiac […]
Cognitive Impairment
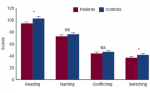
Cognitive impairment (CI) is frequently associated with critical illness and can be defined as the loss or decline of higher mental functions (memory, attention, calculation, language, orientation and speed of information processing) that modify a person’s activity and social interaction. CI is additionally defined as self- and/or informant-reported involving decreased ability on cognitive tasks and/or […]
Headache
Selective attention is defined as the preferential allocation of cognitive and neural resources to a specific event that has become behaviourally relevant.1 Attention is a prerequisite to all cognitive tasks and learning. It involves many brain structures grouped into the so-called attentional matrix. Migraine is frequent and occurs in as high as a quarter of […]
US Neurology Highlights
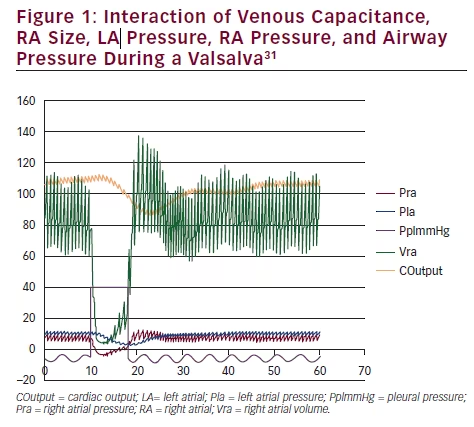
Patent foramen ovale (PFO) is an opening or flap in the atrial septum that exists as a normal and vital component of intrauterine life. PFO allows for the transportation of rich oxygenated blood to bypass the lungs and flow from the right to the left atrium during fetal development. Shortly after birth, a reduction in […]
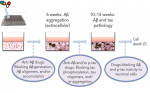
Recapitulating Amyloid β and Tau Pathology in Human Neural Cell Culture Models—Clinical Implications
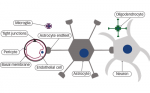
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease, clinically characterized by progressive memory loss. To date, an estimated 5.2 million people have the disease in the US, and the total number of people with AD-related dementia is projected to rise to 13.8 million by 2050.1,2 At present, there is no cure for the disease, […]
Significant advances in understanding the genetic mechanisms behind epilepsy have been made in the past 20 years, especially in the case of epileptic encephalopathies. Though approximately 20–30 % of epilepsies can be attributed to an obvious acquired etiology, such as stroke or traumatic brain injury,1,2 genetic factors are estimated to underlie 40–70 % of all […]

Trending Topic
Seizures are one of the most frequent neurological disorders in neonates − the incidence of seizures in infants born at term is 1–3 per 1,000 live births, and is even higher in both preterm and very-low-birth-weight infants at 1–13 per 1,000 live births.1 Seizures may signify serious malfunction of, or damage to, the immature brain and […]
Journal Archive
European Neurological Review is a peer-reviewed, free-to-access, bi-annual neurology journal comprising review articles, case reports, practice guides, theoretical discussions, and original research. It features balanced and comprehensive articles written by leading authorities, addressing the most important and salient developments in the field of neurology in practical terms.
Latest articles videos and clinical updates - straight to your inbox
Log into your Touch Account
Earn and track your CME credits on the go, save articles for later, and follow the latest congress coverage.
Register now for FREE Access
Register for free to hear about the latest expert-led education, peer-reviewed articles, conference highlights, and innovative CME activities.
Sign up with an Email
Or use a Social Account.
This Functionality is for
Members Only
Explore the latest in medical education and stay current in your field. Create a free account to track your learning.